Yauhen Zaremba, Director of Demand Generation tell us, “Put simply, a higher ROI indicates you are productively managing your balance sheet and generating profit. A higher ROI also indicates that your business requires minimal investment for maximum profit. However, it’s important to keep in mind that it shouldn’t be the only metric you measure for profitability. Keep in mind your cash flow, liabilities and ROE to get a full picture of your business’s financial health.”
Looking for ways to grow and scale your business? Want to boost your profitability? We’ve got a game-changing metric that can help: return on assets (or ROA for short).
ROA helps you understand how profitable your business is in relation to the assets you own. Why is this essential?
By analysing this metric, you can gain critical insights into how effectively you’re using your assets to generate revenue. Once you’ve learned how to calculate your ROA and improve upon it, you can ensure you’re making the most of what you have and maximising profits.
In addition, if you plan to sell any assets in the future, knowing how to calculate your ROA is crucial for ensuring you get the best value for your sale. Knowing your ROA, you can confidently negotiate the best price and ensure you’re not leaving any money on the table.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to calculate ROA for your small business, while highlighting some factors that can affect it.
Let’s get started!

Factors that can affect ROA
We’ve already established that ROA is essential for comprehending your profitability. However, it’s not set in stone. Here are some main factors that can affect your ROA.
Asset utilisation
Asset utilisation is all about making the most out of what you have. If you’re using your assets well, you’ll have a higher ROA. If not, your ROA will suffer.
Let’s say you own a car hiring service and have a rental agreement form that you’re not utilising to its fullest potential. Maybe customers aren’t filling out the form or perhaps they’re providing incomplete or inaccurate data—both of these could negatively impact your ROA.
Operating expenses
Operating expenses can take a toll on your profits and, ultimately, your ROA.
Let’s say you run a small software company. Your operating expenses could include things like salaries, rent, software, and office supplies. Your ROA will be negatively affected if these expenses are eating into your profits.
This is where making savvy business decisions such as utilising free PDFPlatform services online can be beneficial. Free but effective tools like this are a great way to reduce unnecessary operating expenses.
Capital structure
If you’re not careful with your capital structure, it can negatively impact your ROA.
Your capital structure refers to how you fund your operations. For example, you could do this through debt or equity financing. Too much debt and not enough equity can lead to high interest payments and financial instability, which can drag down your ROA.
In addition, if you rely too heavily on equity financing, it can lead to a dilution of ownership and lower return on investment.
Let’s say you run a small tech startup. If you’ve relied too heavily on debt financing to fund your operations, you could find yourself struggling to make your interest payments and falling behind on bills. This could hurt your business’s ability to grow and generate profits.
Industry conditions
The industry you operate in can also impact your ROA.
For example, if you’re in a highly competitive industry like sales, you may need to invest more money in unique digital marketing strategies and promotions to stand out from the crowd. This can increase your expenses, and therefore decrease your ROI.
Economic conditions
The state of the economy will inevitably impact various aspects of your business—and that includes your ROA.
When the economy is doing well, people may be more willing to spend money on your products or services, leading to higher revenues and a higher ROA. However, if the economy is struggling, people may be more cautious with their spending, resulting in lower revenues and a lower ROA.
Competitive landscape
Various sectors and industries are becoming increasingly competitive. While competition can be good for business, it can also impact your sales and profits. In turn, this will affect your ROA.
So, if you’re facing fierce competition for your retail store in Australia, for example, you may need to differentiate your offerings or adjust your prices to stay competitive.
Lowering your prices can eat into your profits, leading to a lower ROA. However, if you’re in a niche market with few competitors, you may be able to charge higher prices, resulting in a higher ROA.
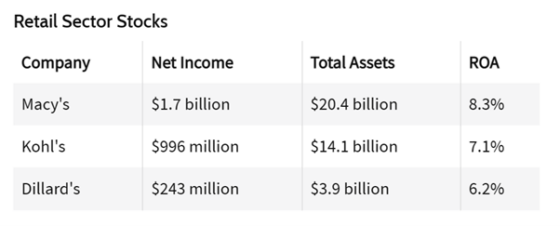
Image sourced from investopedia.com
ROA = Net Income / Total Assets
To calculate ROA, you take a company’s net income and divide by its total assets, then multiply by 100 to find the percentage.
Let’s see this in action.
If you own a small business that sells $100,000 in net income and has $500,000 in total assets, your ROA would be 20% ($100,000 ÷ $500,000 = 0.2 or 20%).
This means that for every dollar the business invests in assets, it earns 20 cents in profit.

Limitations of ROA as a sole indicator of profitability
When it comes to measuring profitability, ROA is a handy tool. But remember, it’s not the be-all and end-all. Why?
Firstly, ROA doesn’t take into account external factors like changes in the economy or shifts in the market. These factors can have a massive impact on a business’s financial performance and aren’t captured by the ROA calculation.
Secondly, ROA doesn’t factor in a business’s liabilities, such as debts or accounts payable. So even if your business has a high ROA, you could still be struggling financially if you have a lot of debt to pay off.
Finally, ROA doesn’t give any information about your business’s cash flow, which is crucial for understanding how much money you have to pay bills and invest in future growth.
To get a more complete picture of your business’s financial health, consider ROA as one piece of the puzzle. You should also look at Return on Equity (ROE), cash flow, and net profit margin.
Coming to terms with the true utility of ROA
Coming to terms with Return on Assets (ROA) is essential for assessing your company’s financial performance. Consider it a measurement of your business’s efficiency.
Put simply, a higher ROI indicates you are productively managing your balance sheet and generating profit. A higher ROI also indicates that your business requires minimal investment for maximum profit.
However, it’s important to keep in mind that it shouldn’t be the only metric you measure for profitability. Keep in mind your cash flow, liabilities and ROE to get a full picture of your business’s financial health.
In addition, when comparing ROA, be sure to measure figures against competitors in your industry that may share the same asset base.
No matter the size of your business, you can start measuring your ROA today to determine how efficient your company really is.

Yauhen Zaremba is the Director of Demand Generation at PandaDoc. He’s been a marketer for 10+ years, and for the last five years, he’s been entirely focused on the electronic signature,
proposal, and document management markets. Yauhen has experience speaking at niche conferences where he enjoys sharing his expertise with other curious marketers. And in his spare time, he is an avid fisherman and takes nearly 20 fishing trips every year.

Leave a Reply