There’s a follower-following count but it’s not Instagram. A sidebar shows who is trending but it’s not Twitter. One can use emojis to display current status but it’s not WhatsApp.
It has several elements of a popular social media platform, but it is not one.
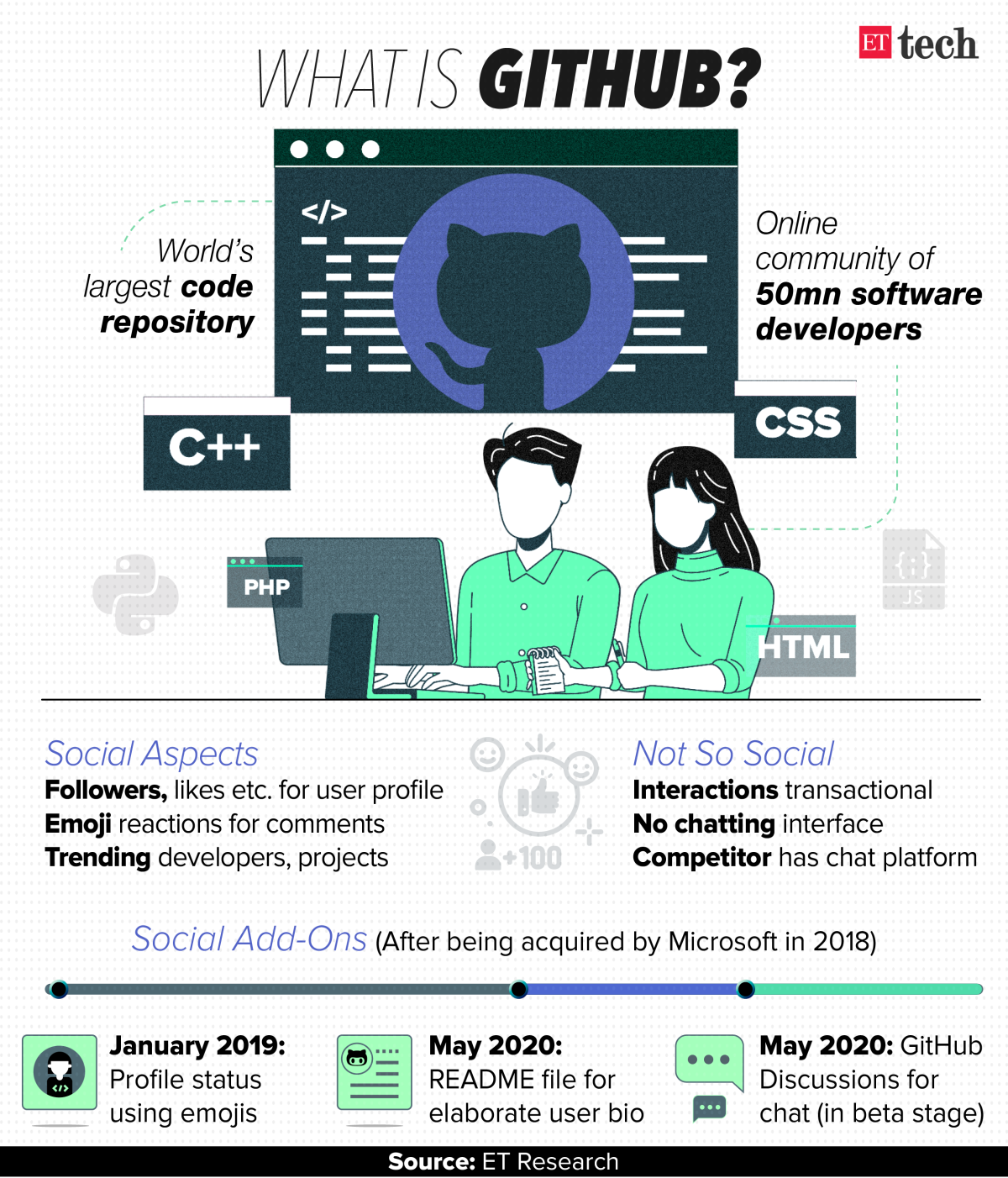
This is GitHub, the world’s largest code repository platform online. A platform used by some 50 million software developers to host their coding projects, most of them open-source — meaning others can access their codes and modify them to create better versions if they feel like.
Most of the internet is produced or hosted on GitHub in the form of code. “What Gmail is to email, GitHub is to writing software,” says Kiran Jonnalagadda, cofounder of HasGeek, a platform to build and discover peer groups.
Inside GitHub, developers can create their own “repository” of coding work. If the said repository is in the open-source domain, other developers can access it. They can “star” it to show interest, or download it for their use. Many “commit” to it to make it better, and send a “pull request” to the host for a consensus to enrich the main version or to keep a separate branch. Some even “fork” it by creating an entirely different codebase for their own experimentation.
The platform allows developers to collaborate with fellow developers from around the world. Like Jugal Mistry, a Mumbai-based freelance web developer, who has never worked in a company to know what having colleagues feels like. On GitHub, however, he has worked with developers from countries like Japan, Russia, and the US, to name a few. “These are strangers with a common goal, of wanting to make the code work or get better.”
For a community that stays isolated from the mainstream world and never gets its moment under the sun, “GitHub is where developers find their place to discuss, enhance, learn and collaborate with people who essentially understand who they are and what they do. A community which was a long time coming and still has a long way to go,” says Soumya Sinha, Delhi-based data manager at a multinational consulting firm.
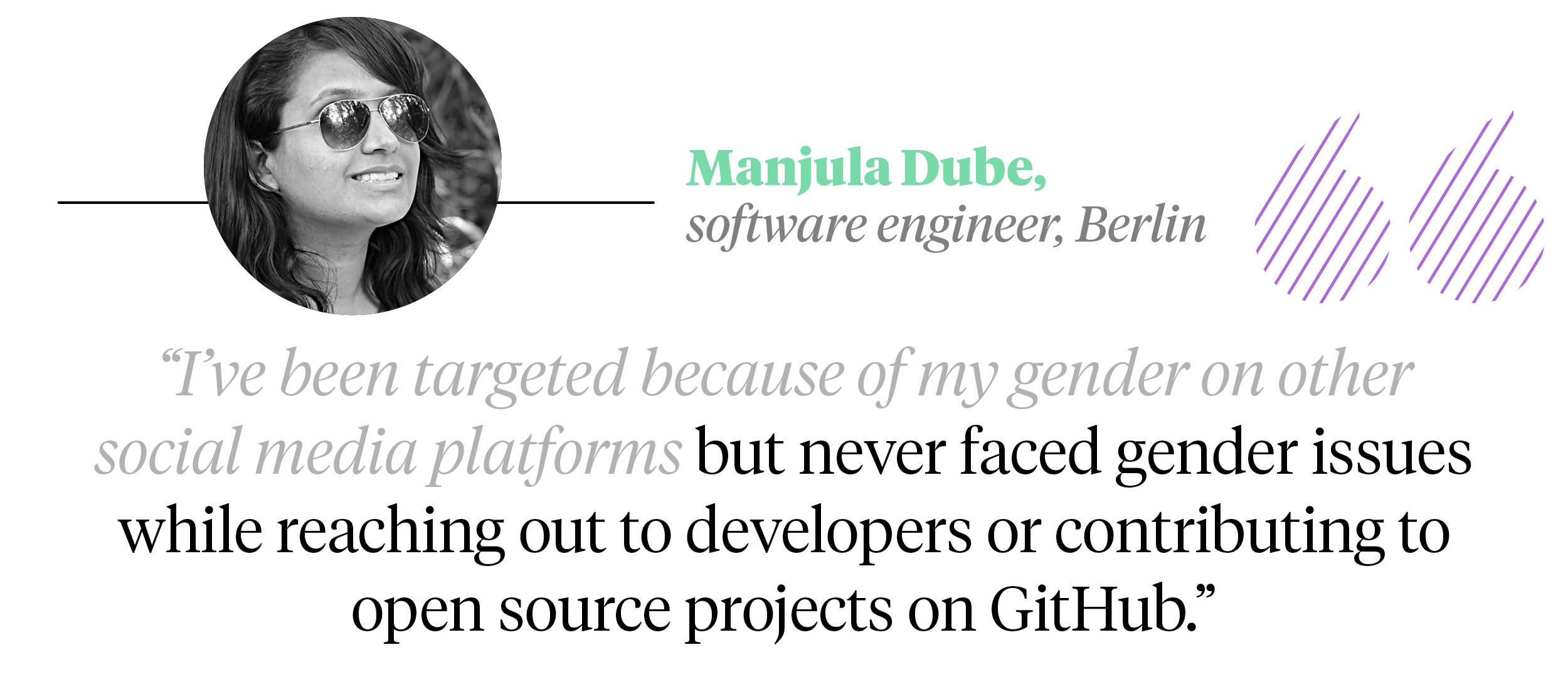
GitHub’s construct leaves little room for gender bias, say a few women developers on the platform. “I’ve been targeted because of my gender on other social media platforms but never faced gender issues while reaching out to developers or contributing to open source projects on GitHub,” says Manjula Dube, a Berlin-based software engineer. Sometimes you can’t even tell the gender of a person on GitHub, adds Akanksha Vyas, a Mumbai-based developer. “People are much more conscious of their gender while posting on networking communities for developers instead. Because they may get a “you don’t know anything” comment there,” says Vyas.
Inside this community, developers get their due as every commit gets recognised, every accepted pull-request gets them a credit. Even then, “pull-fork-commit-stars are just keywords. It’s like a society with a rulebook, what matters to them is being a part of that society,” adds Sinha.
That said, stars on their projects or profiles, an equivalent of social media “likes”, are still coveted by many.
What YouTube is to content creators or Instagram is to influencers, GitHub is to developers around the world. It is here that they find validation and a means to express themselves in the language(s) they know best — Java, Python, C, Ruby,… you get the drift.
“Within the programmers’ community, a solid GitHub profile is a badge of honour as people know you can’t ‘fake it till you make it’ on that platform,” says Prashant Singh, former VP – product at Paytm.

However, the social layer to GitHub is crude and purely incidental, Singh points out. The interactions with developers are largely transactional. “They are your best friends, but only until the code starts working. Then they’re gone,” says Mistry.
GitHub is also different from social media in that platforms like Instagram are where you present a polished version of yourself, adds Singh. In the developer world, on the other hand, “things are always improving.”
Switch to Social
Over the last couple of years though, Microsoft has been trying to make GitHub more social.
The tech conglomerate, which acquired GitHub in June 2018, has actively launched features since then to make the platform seem more socially interactive.
In May, GitHub said it would launch GitHub Discussions, a chatting interface that allows developers to have conversations within the platform.
Simultaneously, it introduced an add-on feature called README that enables users to mention elaborate details of their coding work and background on their profile using text and pictures — the rest of the platform is fraught with coding languages.
Last year, GitHub added another aspect to enhance the social quotient of the platform, by allowing users to set their profile status using emoticons.
It also introduced a ‘Sponsor’ button to enable users to financially support developers in their open-source software projects. These are projects that have made available source codes for anyone on the platform to access and modify.
“You can also host a website on GitHub without paying for domain charges,” says Prathmesh Bhansali, a third-year engineering student from Amravati in Maharashtra.
“We are empowering [developer] communities to socialise on GitHub in a way that feels less fragmented and belongs to them. We see value in helping communities create a space that helps folks learn, support one another and be recognised for all of their contributions beyond code,” says Becca Zandstein, senior product manager at GitHub, in an email.
Developers in India — the third-largest developer community on the platform after the United States and China — feel this is in response to developers around the world gravitating towards external platforms built on top of GitHub for networking and conversation.
These include platforms like Gitter and Stack Overflow where developers discuss coding projects with individuals or in communities.
Late to the Chat Room
GitHub Discussions, still in the beta stage, aims to beat the likes of Gitter — a six-year-old networking platform owned by GitHub’s rival GitLab.
Developers use their GitHub account details to sign in to and access Gitter.
A foreign developer who wishes to stay anonymous, says that GitHub has had a history of building products they never released. “They had a chat product in the works, but Gitter had already come up before they could launch it. And at that time, they wanted to encourage the ecosystem around GitHub instead of crushing it with their own product.” GitHub did not respond to a specific query on Gitter.
Many developers feel that not launching a synchronous communication interface on the platform sooner is a miss on GitHub’s part. “Developers have gotten used to other software for chat now,” says Ajey Gore, a Singapore-based tech entrepreneur and former CTO of multi-service tech platform Gojek.
However, Gitter has just over 1.5 million developers on board at present, which is roughly 2% of GitHub’s developer user base of 50 million.
Even though the numbers aren’t big, some developers feel a chat software is essential to a platform like GitHub to enable collaborations.
“Without chat, reaching out to people gets tough sometimes because not every developer mentions their email address on their GitHub profile,” says Vyas from Mumbai who is also the director of global community Women Who Code’s Mumbai chapter. “For me, GitHub is not social yet because there’s no in-built chatting interface as such.”

Mistry, too, agrees in principle. But experiences can alter principles sometimes.
“A friend recently went off social media due to personal issues,” he recalls. “I couldn’t trace him for two months and was genuinely concerned about his well being.”
Then he saw his friend had been active on GitHub, having made two commits in three days, releasing changes into the world. “I was relieved because I knew as long as he’s coding, he is going to be fine.”
(Illustration and graphics by Rahul Awasthi)
Leave a Reply