Launched in 2009, the Bluetooth Low-Energy (BLE) technology set the base for the future of applications in the Internet of Things (IoT), primarily focusing on those that require minimal power consumption.
In 2017, Bluetooth SIG announced the Bluetooth Mesh standardising several BLE features, where the end goal was to amplify the human potential in every way possible in today’s digital era, says Tarun Thomas George, co-founder & COO of Cavli Wireless
The evolution of bluetooth technology
In the beginning, this technology was used generally for audio data streaming and file transfer, but it has matured over the last 20 years. At present, Bluetooth devices have become an indispensable part of our life and can be found in speakers, headphones, smartphones, smart TVs, smartwatches, etc.
Moreover, Bluetooth technology is constantly improving, so it has evolved and is recognised as one of the most important wireless communications pillars for the Internet of Things (IoT).
Bluetooth is a wireless communications technology for short-range, point to point and point to multipoint transmissions, that operates in the unlicensed Industrial, Scientific and Medical (ISM) designated 2.4 GHz RadioFrequency (RF) band for ease of usage.
It was standardised within the IEEE 802.15.1 protocol but no longer maintains the standards, rather, is being developed and managed by the Bluetooth Special Interests Group (SIG), a 35,000 member company group from different areas of telecommunication, computing, networking, and consumer electronics.
BLE technology for the Internet of Things
Applications
In order to meet market needs, wireless technologies permanently continue to transform. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) has been introduced from Bluetooth 4.0 and was designed in order to meet the IoT utilisation needs. Compared to traditional, classic Bluetooth performances, BLE is optimised for short bursts of data transfer, from different kinds of sensors.
It provides long-range, lower latency and power consumption, higher throughput (up to 2Mbps), and more adaptable IP access and mesh networking support compared to previous generations of the Bluetooth protocols. In the field of Industrial IoT and Medical IoT, low-powered devices are the backbone of the system and BLE is best suited for those applications.
BLE technology is embedded in many types of IoT devices applicable to home, wellness, sports, gaming and automation, medical and industrial electronics. Since backward compatibility is provided with BLE, broadly all new devices that support BLE also support the classic Bluetooth as well and vice versa.
Mesh networks in BLE
Mesh networking features are exceptionally important for IoT use cases. Quite the opposite from the traditional Bluetooth topology, where all Bluetooth devices are connected to a central hub or the Master node. In BLE networks, Mesh topology enables the mutual communication between all nodes – devices within the range.
Together with support for an almost unlimited number of network subscribers in a single BLE network, this feature extends the network coverage, increases the robustness, and at the same time protects the network from the single point of failure.


How bluetooth and cellular LPWAN can inter-operate for maximum benefits
Bluetooth Low Energy devices offer several advantages for the deployment of low power IoT devices for a myriad of use cases and applications but its shortcomings such as the low operability range and low data throughput thus limit its applications to only short-range devices.
To build a system of IoT devices that are capable of overcoming the shortfalls of individual communication technologies used, it is more practical to combine different technologies to cover each other’s drawbacks while adding on top of the advantages of each of them for a more versatile end system of devices.
Cellular IoT connectivity is one of the most popular technologies for the IoT industry owed to its numerous advantages such as long-range, high data throughput, security features, ease of deployment, and more. It overcomes the drawbacks of BLE technology.
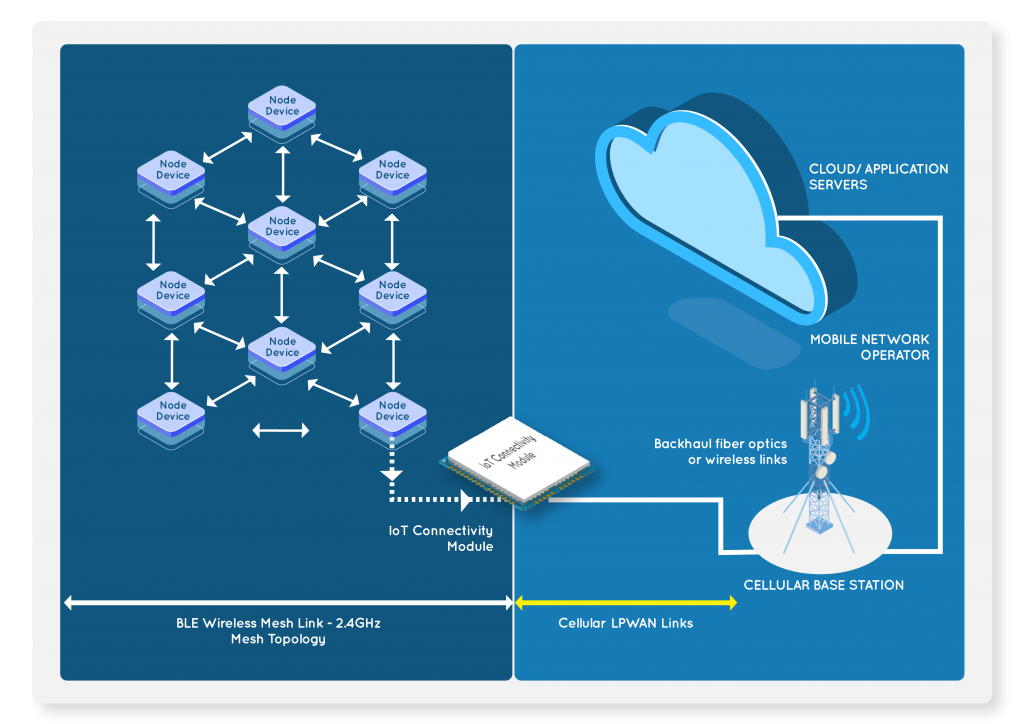
In an IoT system where both cellular connectivity & BLE are deployed, the BLE devices can act as the primary communication network which enables devices to talk to each other in a mesh network topology while also being able to communicate to nearby classic Bluetooth devices such as a Bluetooth enabled phone and at the same time, reduces the cost per device on hardware and network charges.
The end data stream can be sent to the internet with a cellular gateway that acts as a gateway modem between the BLE nodes and the internet.
An effective use case of using BLE paired with cellular LPWAN is smart metering. In a scenario where several smart metre nodes are deployed in a locality, an efficient solution can be made by creating a mesh network between the different smart metre nodes where each node is connected with BLE technology.
With all the node devices connected with the BLE mesh network, a gateway device with cellular LPWAN connectivity can be placed as the last-mile connectivity device that receives the data from the mesh network and relays it to the cloud. In this scenario, only one device is required to actively connect to the cellular network and communicate with the cloud which allows for more efficient networking infrastructure.
This technical symbiosis brings together the benefits of both wireless technologies and offers a modular, scalable, and adaptable network solution necessary for IoT connectivity. It makes a hybrid core network, supported with mesh topology performance due to the BLE technology support & at the same time, cellular connectivity additionally extends the available network coverage and overcomes typical BLE mesh network challenges such as low-range.

Conclusion
To enable the next generation of IoT solutions, enterprises would need to consider different choices of connectivity, even hybrid connectivity for increased network efficiency while bringing down the costs.
Bluetooth Low Energy technology is a promising short-range connectivity option for IoT devices with the ability to operate alongside long-range, high throughput connectivity options like cellular LPWAN that opens up a new frontier of smart devices that are smaller, more power-efficient, and cost-effective.
A synergetic relationship between BLE technologies and Cellular LPWAN is one of the ways that IoT enablers are going to take advantage of in the future to enable use case scenarios that weren’t feasible till now.
The author is Tarun Thomas George, co-founder & COO of Cavli Wireless.
Comment on this article below or via Twitter: @IoTNow_OR @jcIoTnow
Leave a Reply